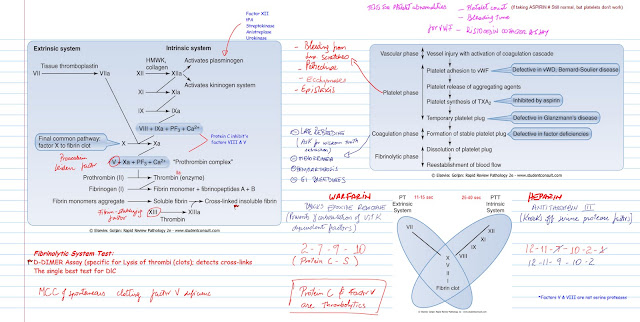
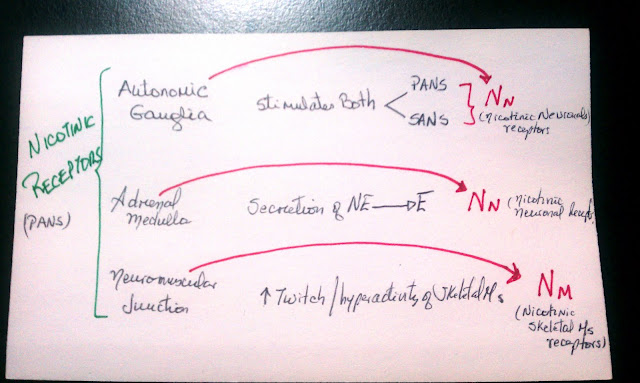
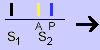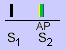Stenosis = problem in
opening the valve
Regurgitation = problem in closing the valve
Need to know where valves are heard best – right 2ndICS (aortic valve), left 2nd ICS (pulmonic), left parasternal border (tricuspid), apex (mitral) – this isn’t necessarily where the valve is, but where the noise is heard the best.